Road and Railway Infrastructures
Retaining walls, tunnels, underpasses, bridge abutments.
Steel sheet piles are commonly used to build road and railway infrastructures. It is a cost-effective solution for:
- retaining walls;
- tunnels and underpasses;
- bridge abutments.
They can achieve a service life of up to 100 years in normal soil conditions, and bear high vertical loads.
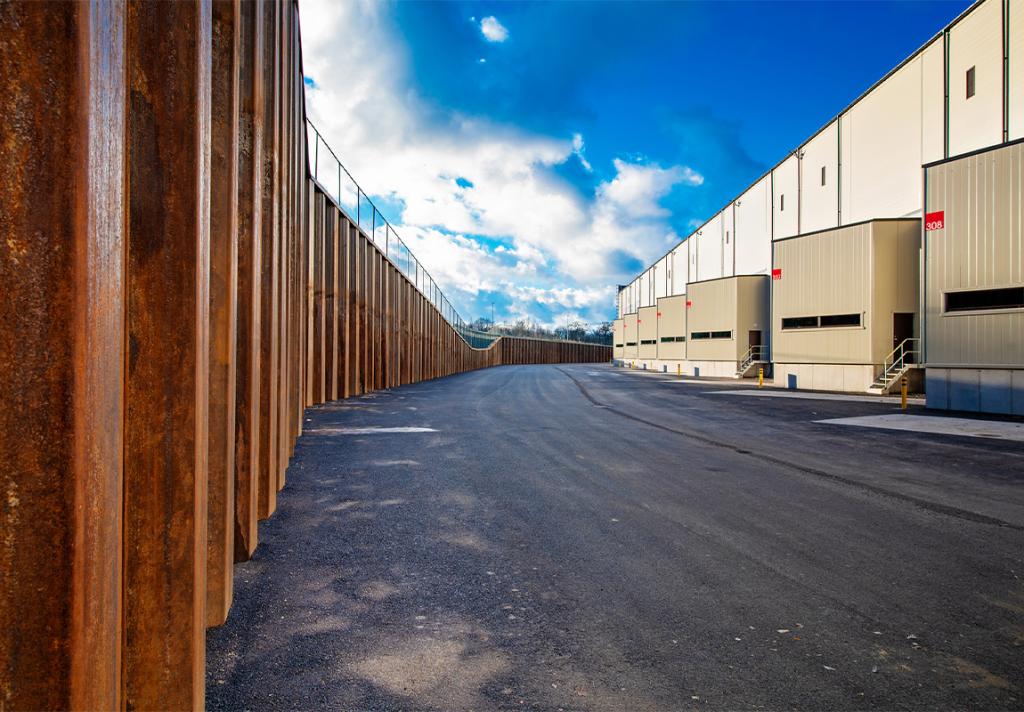

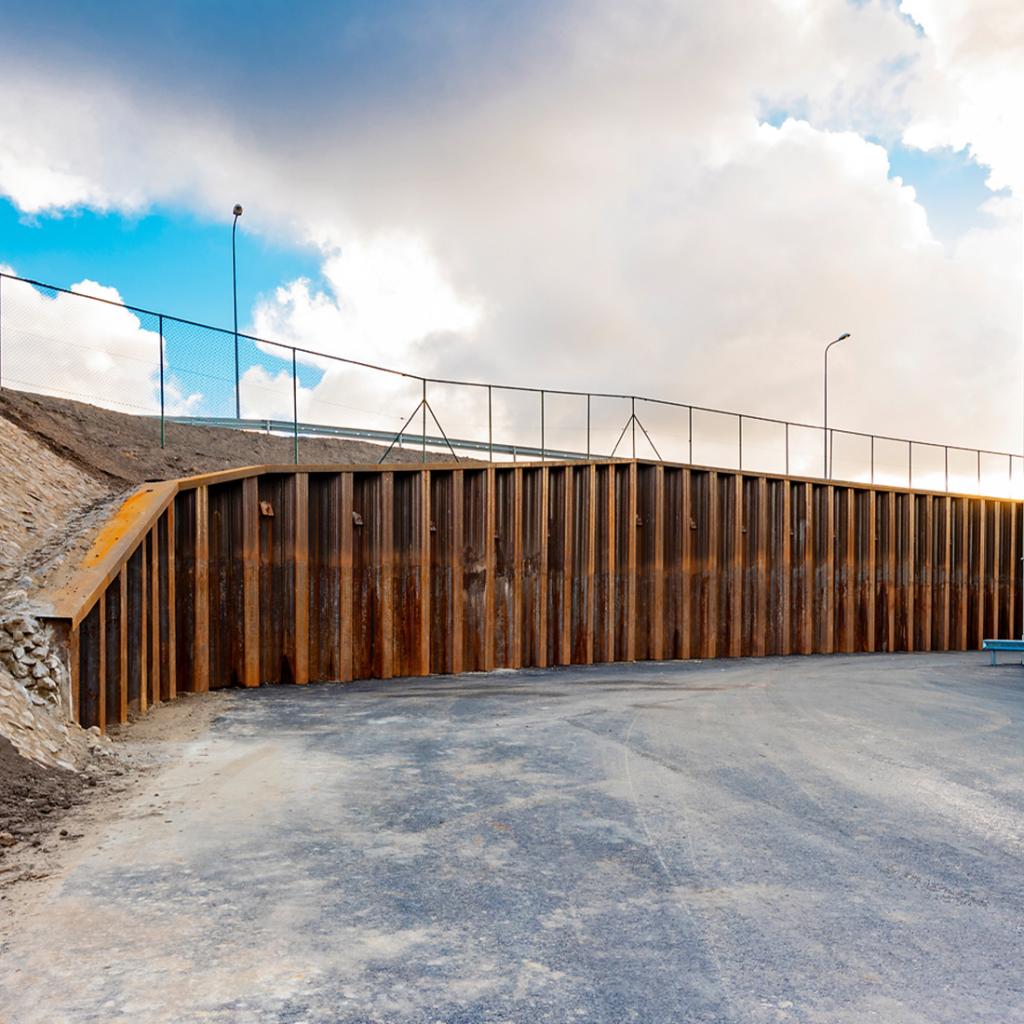
Retaining walls
A retaining wall is a sturdy structure that provides lateral support to soil and water masses, thereby retaining the land at different levels on either side of the wall. Retaining walls are primarily used for altering the elevation of the surrounding terrain for a variety of purposes, including construction of road and rail lines, landscaping, and building construction. Additionally, they are capable of transmitting substantial vertical loads to the ground, similar to bearing piles.
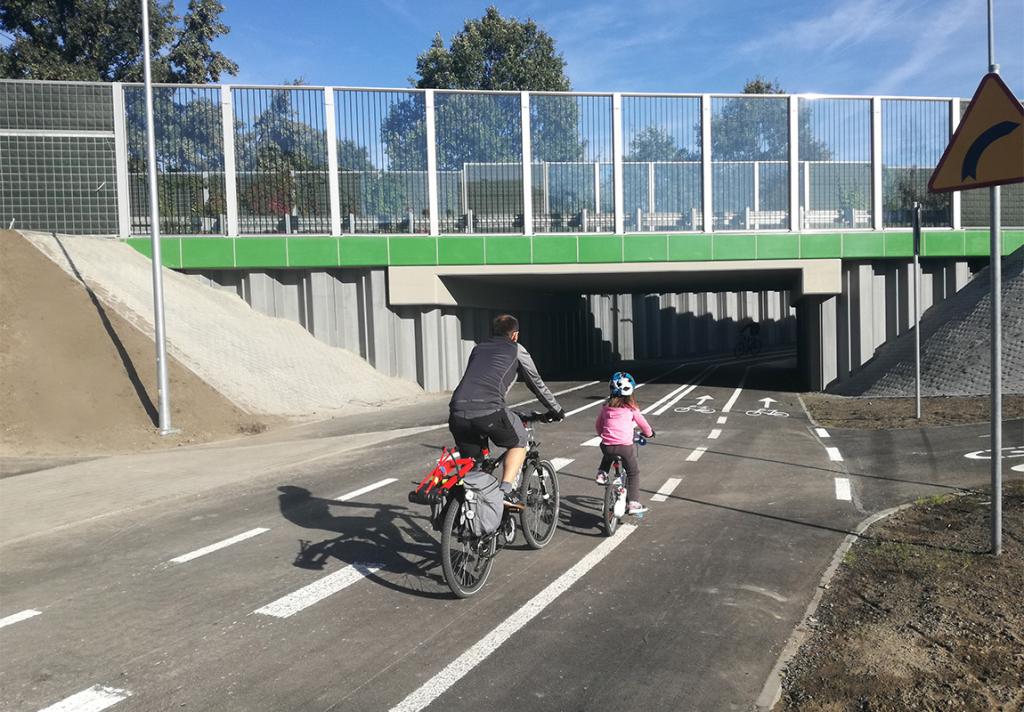

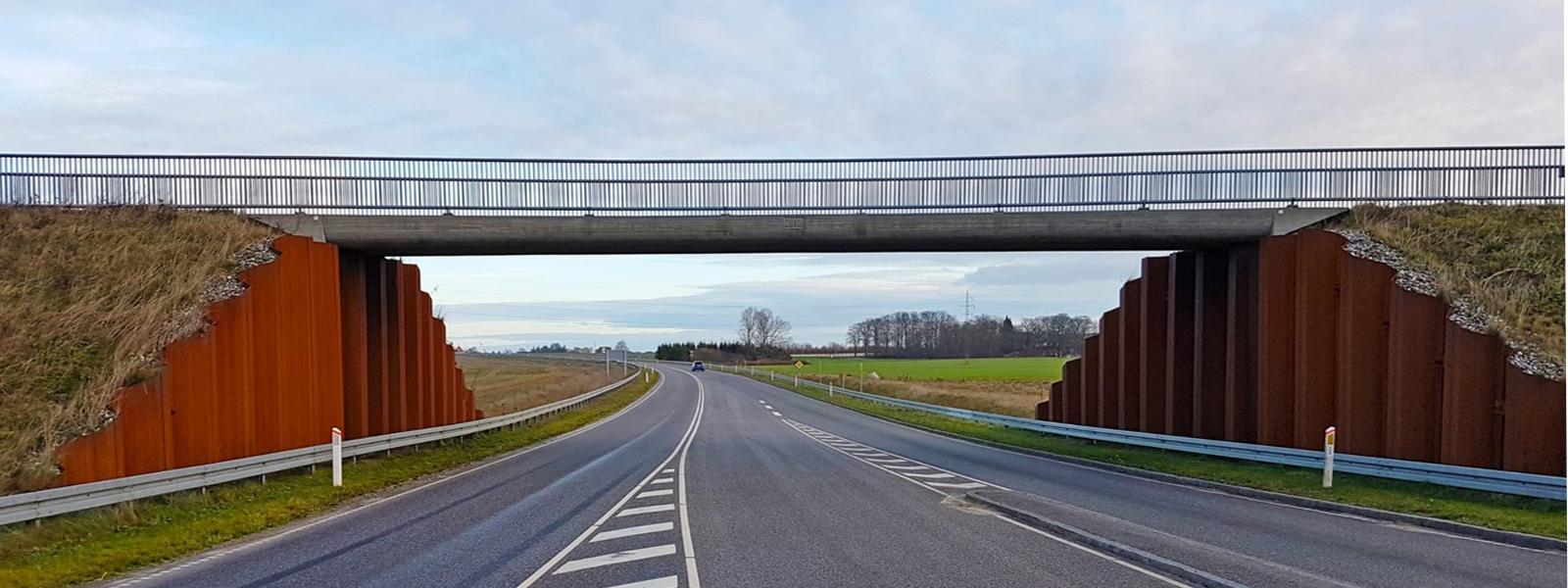
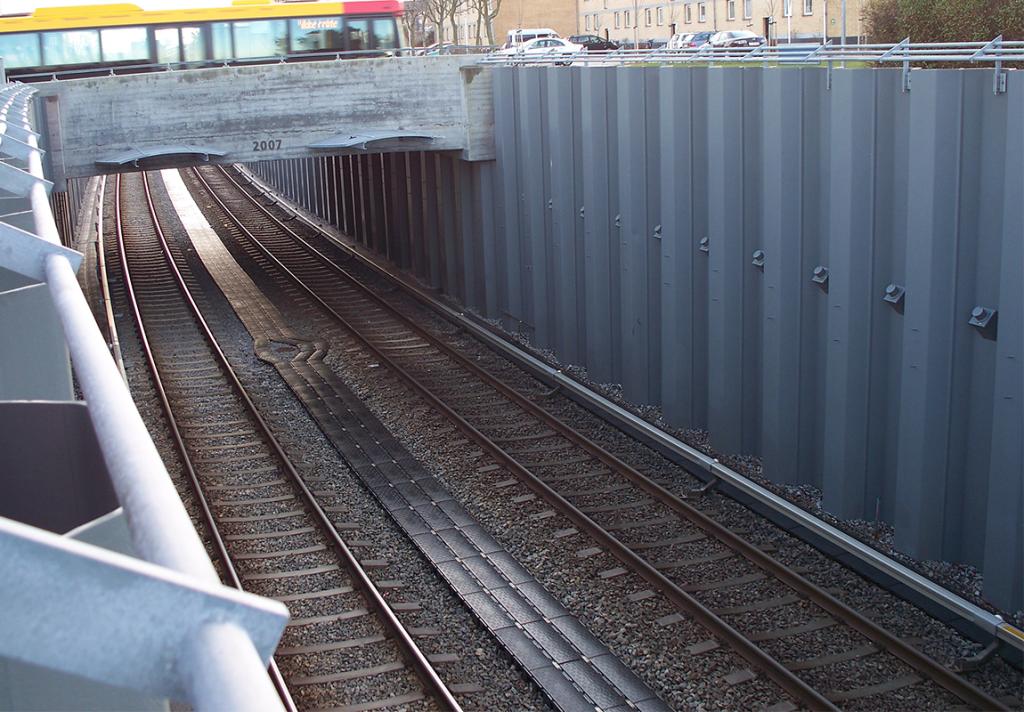
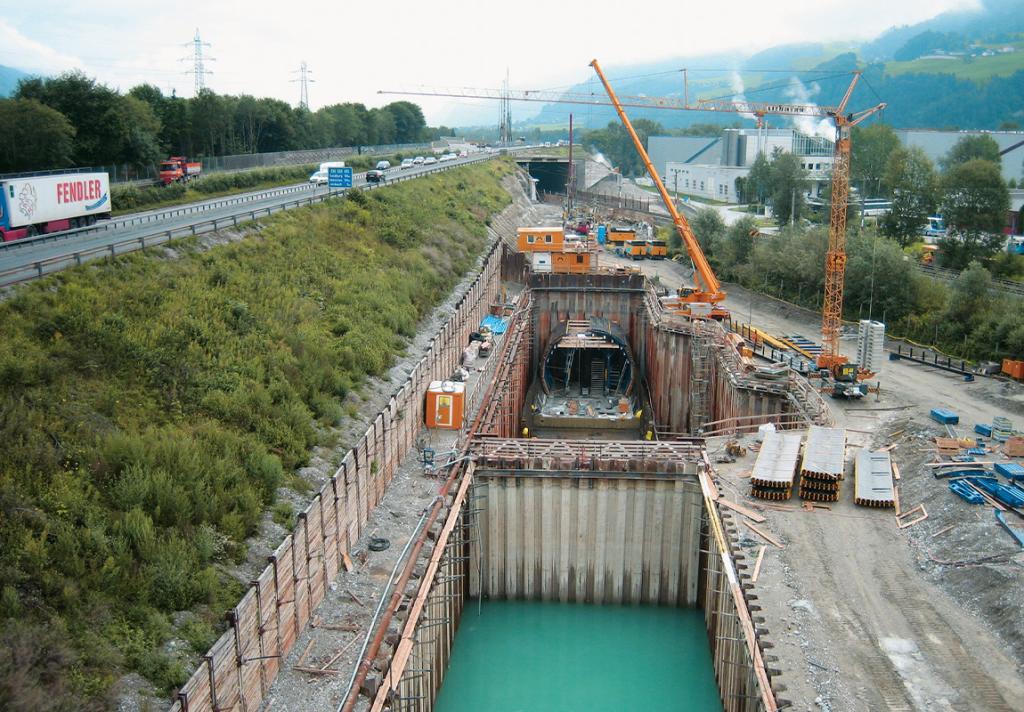
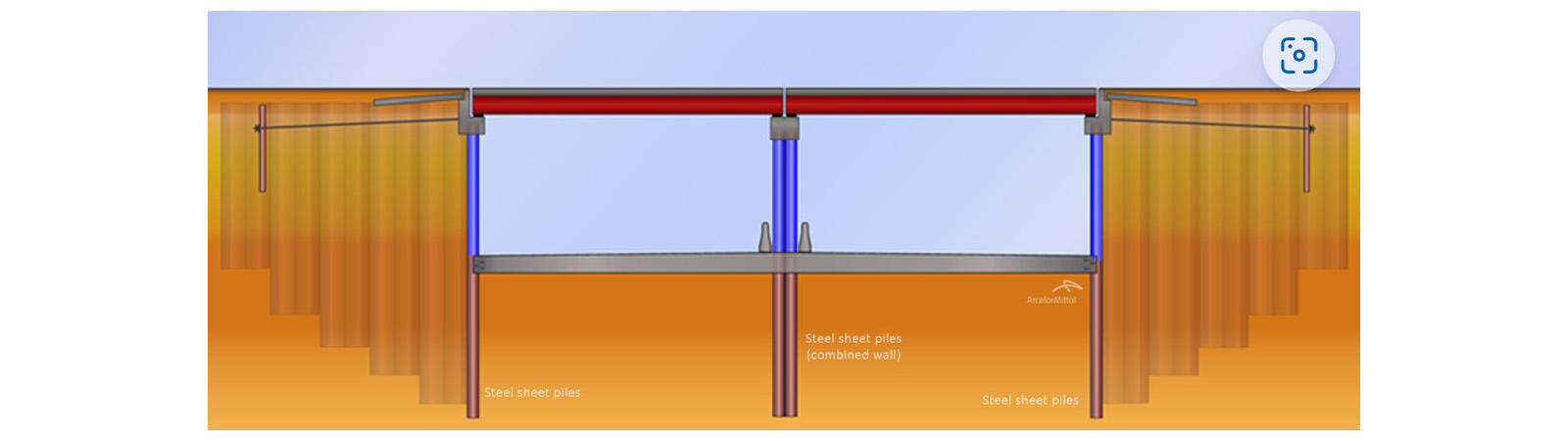
Tunnels and Underpasses
Tunnels are underground passageways, dug through the surrounding soil and enclosed except for an entrance and an exit at each end. As bridges, they are essential for a well-functioning transport network. In urban areas, they are usually built at locations with limited space at the surface.
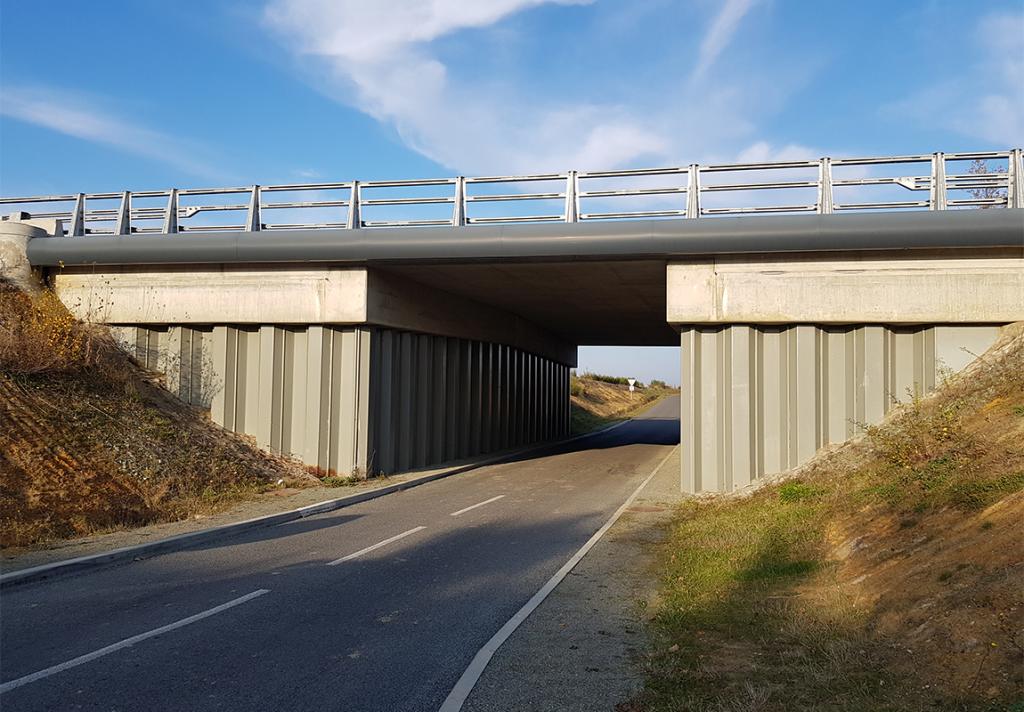
Underpasses are very similar structures, except that they are usually shorter. Underpasses improve traffic flow in traffic intense intersections at the street level, sometimes in combination with bridges. Underpasses are generally designed as a rehabilitation of a crossroad, and hence speed of execution is of utmost importance.
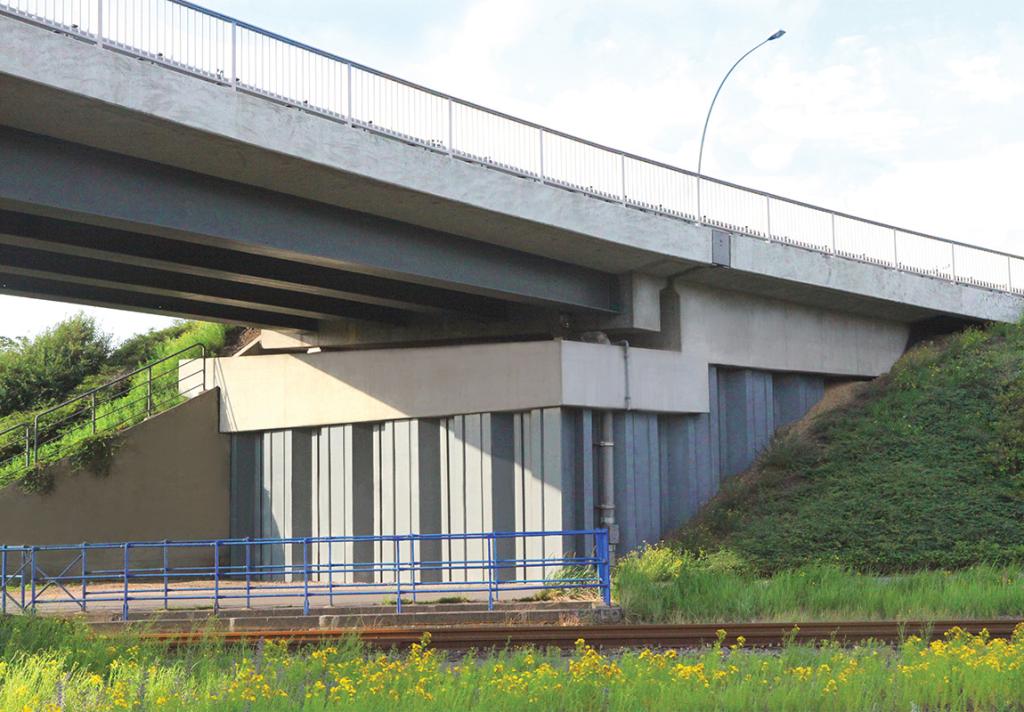

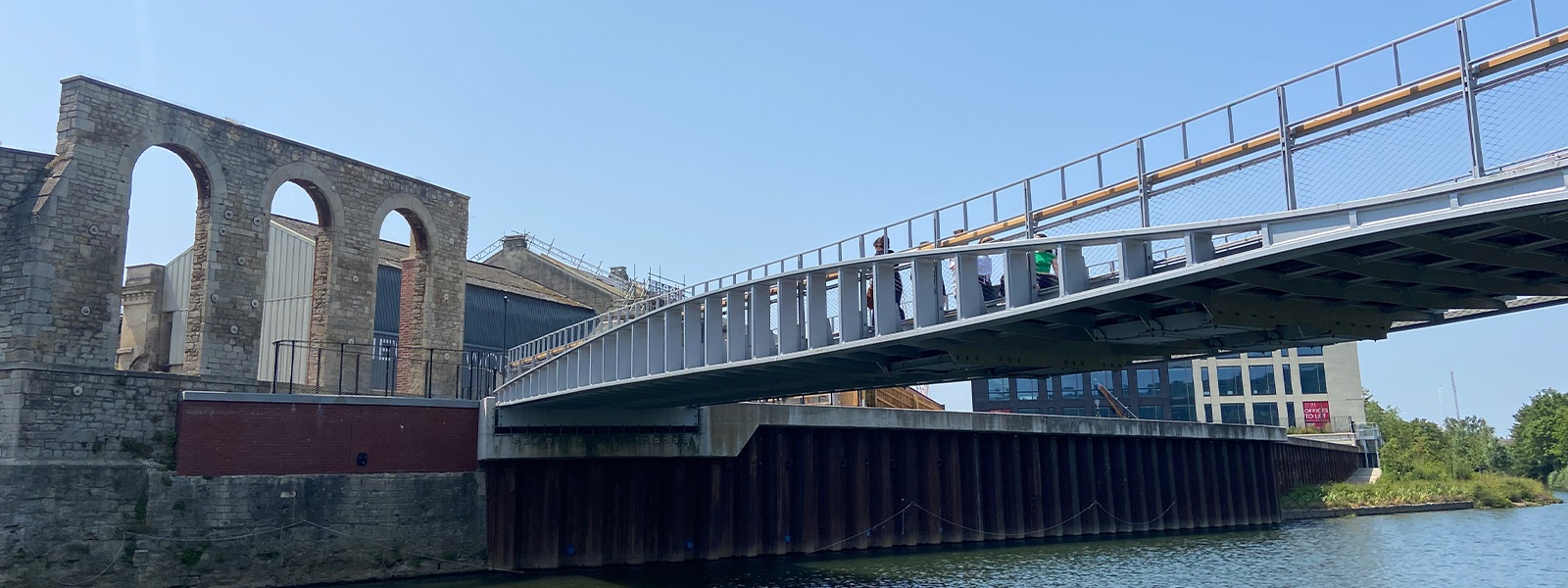
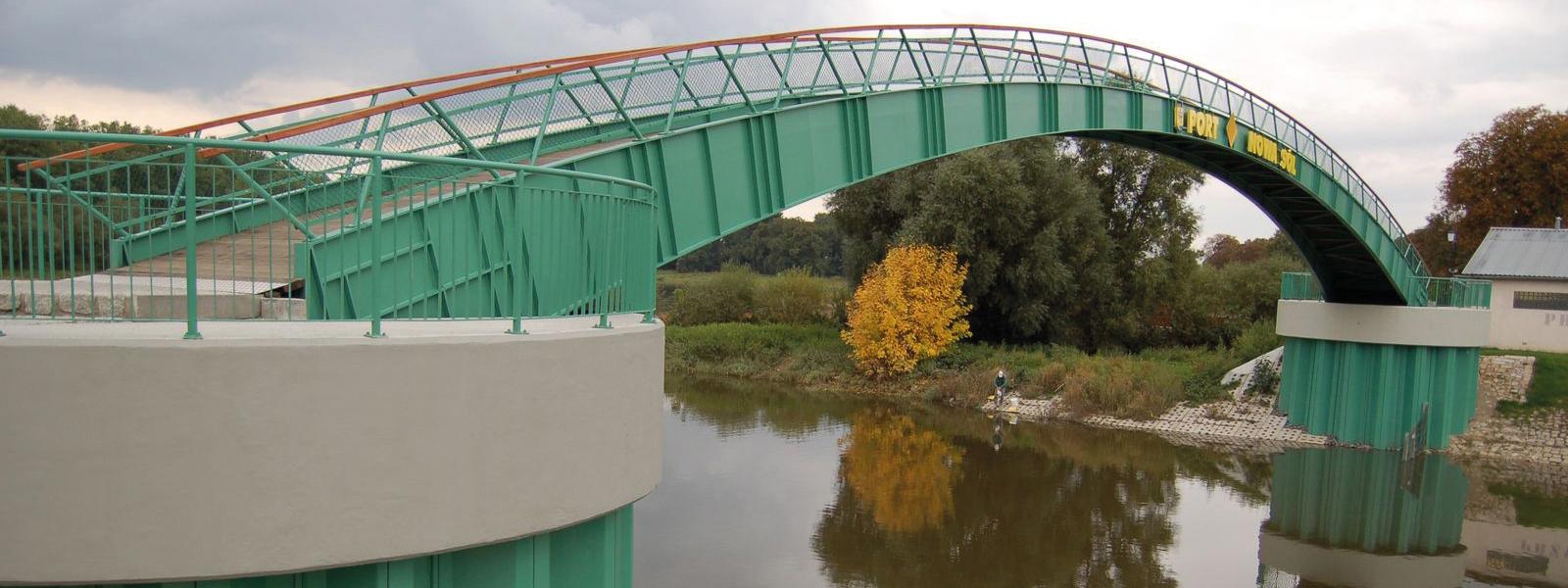
Bridge abutments
Bridges are an essential element of any country’s transportation network, and to keep it healthy, the ability to built and repair bridges quickly is vital. Steel sheet piles offer an accelerated bridge construction method that minimizes the impact to the network. Bridges are built to span physical obstacles to provide a passage over such obstacle. Designs of bridges vary greatly depending on the function of the bridge and the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored.
Retaining Walls
A retaining wall is a more or less rigid wall that supports the soil and water masses laterally so that the terrain can be retained at different levels on both sides of the wall. Fundamentally, retaining walls are used to change the elevation of the surrounding landscape for a variety of reasons, such as road and rail lines construction, landscaping, building construction, etc. They can also transmit significant vertical loads to the ground, in a similar way to bearing piles.
Steel sheet piles walls are relatively flexible retaining walls. Durability and driveability in the ground conditions are an important feature of the design. Structures shall be designed to sustain all actions and influences likely to occur during their execution and service life. Hence, retaining structures must have adequate:
- structural resistance,
- serviceability,
- durability,
- watertightness (especially for pits and excavations).
Steel sheet piles have been used for over a century to build reliable and cost efficient earth retaining structures.

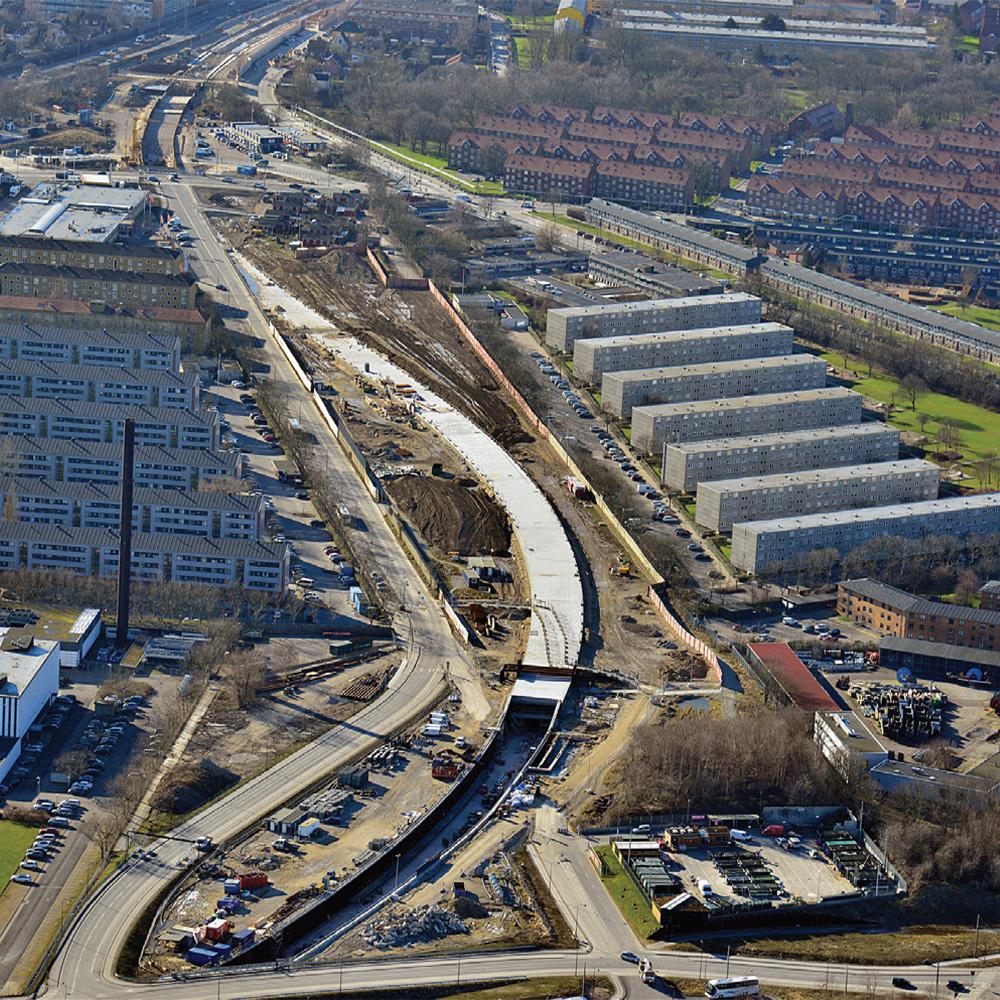
Tunnels and Underpasses
Tunnels are underground passageways, dug through the surrounding soil and enclosed except for an entrance and an exit at each end. As bridges, they are essential for a well-functioning transport network. In urban areas, they are usually built at locations with limited space at the surface.
Underpasses are very similar structures, except that they are usually shorter. Underpasses improve traffic flow in traffic intense intersections at the street level, sometimes in combination with bridges. Underpasses are generally designed as a rehabilitation of a crossroad, and hence speed of execution is of utmost importance.
Hot rolled steel sheet piles are ideal for tunnel and underpass construction, due to:
- faster execution time,
- reduced surface disruption, as no over excavation for foundations is required,
- sheet piles have immediate load-bearing capacity,
- steel sheet piles can be easily made aesthetically attractive,
- guaranteed imperviousness through the use of sealing products or welded interlocks,
- excellent fire resistance performance with and without protection.

Bridge abutments
Bridges are an essential element of any country’s transportation network, and to keep it healthy, the ability to built and repair bridges quickly is vital. Steel sheet piles offer an accelerated bridge construction method that minimizes the impact to the network.
Bridges are built to span physical obstacles to provide a passage over such obstacle. Designs of bridges vary greatly depending on the function of the bridge and the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored.
Bridge abutments have two primary functions
- support the vertical loads of the bridge: the abutments must be able to withstand significant vertical forces from the bridge superstructure,
- act as a retaining wall for the soil that supports the access way to the bridge.